Space Weather Alert - 15th March 2013
What Has Happened?
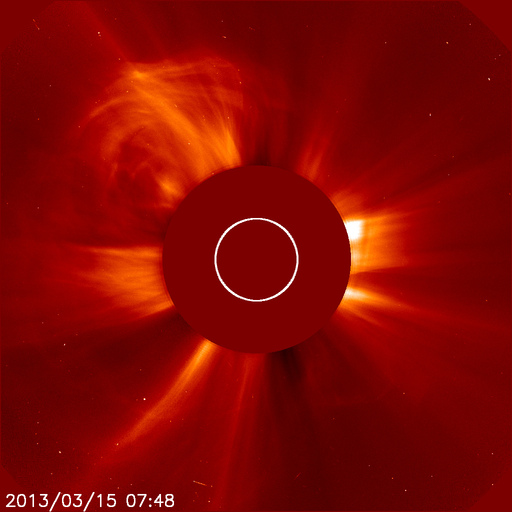
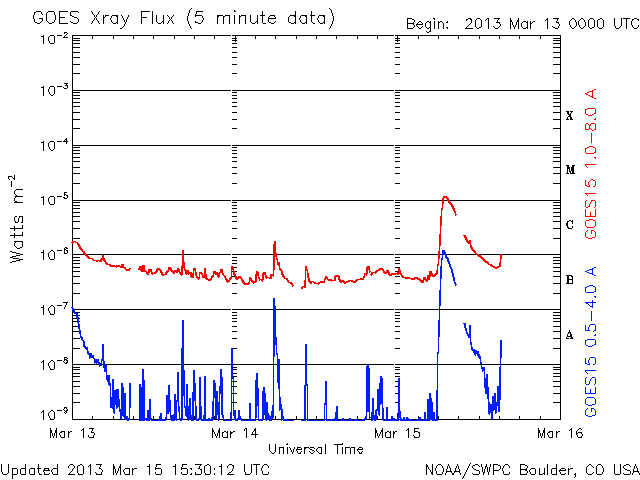
Early this morning (06:00 GMT, 15th) a solar filament eruption triggered an M-class solar flare with an associated coronal mass ejection (CME). This CME is directed towards the Earth and is therefore expected to enhance geomagnetic activity, increasing the likelihood of geomagnetic storms.
The CME could arrive as early as tomorrow night (16th) and could result in enhanced auroral displays during local night time hours, depending on the size of the storm and the solar wind conditions at the time. This is most likely at high latitudes but also at lower latitudes depending on the strength of the storm and assuming clear dark skies.
Sign-up to receive Geomagnetic Disturbance Alert emails.
Follow us on Twitter:
Follow @BGSauroraAlert for more occasional aurora alerts.
Follow @BGSspaceWeather for daily space weather forecasts.
Glossary
- BGS
- The British Geological Survey is one of the Natural Environment Research Council's Research Centres.
CME or Coronal Mass Ejection- The eruption of a portion of the outer atmosphere of the Sun into space, caused by rapid changes in its magnetic field. Often occurs along with a solar flare.
- Coronal Hole
- A region in the Sun’s outer atmosphere (corona) where hot material can flow unrestrained by its magnetic fields out into space.
- Filament Eruption
- An eruption of solar plasma (i.e. ions and electrons) associated with the upward movement of solar magnetic field lines into the corona. Filaments are usually dark against the bright solar disk but can appear bright (as 'erupting prominences') on the limbs of the Sun against the darkness of space. Filaments are often associated with CMEs.
- Flare
- Energy released by the explosive reorganisation of magnetic fields within the Sun's atmosphere.
- High Speed Stream
- A fast moving stream of solar wind, responsible for magnetic storms.
- Magnetogram
- The variation, minute by minute, of the strength and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field. Measured in units of nano-Tesla (for the strength of the field) or in degrees (direction of the field).
Solar Wind- The ever-present expansion of the Sun’s hot outer atmosphere into the solar system, which carries space weather within it.
Sunspot- A region of intense magnetic field in the Sun's visible outer atmosphere often associated with flares and CMEs.