Space Weather Alert - 25 October 2016
What Has Happened?
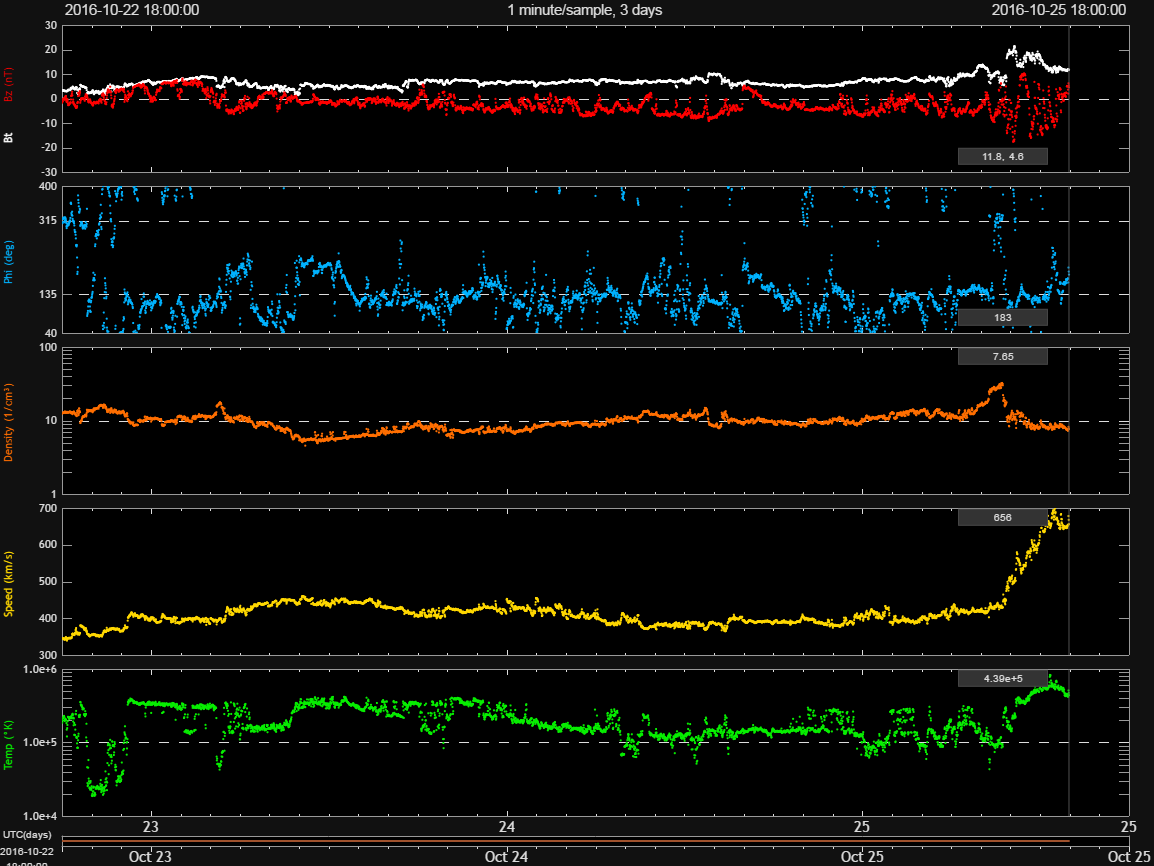
A very large centrally located coronal hole has rotated around the Sun to an Earth-facing position. The Earth is now under the influence of the coronal hole's high-speed solar wind stream that arrived this morning.
Coronal holes can persist for several 28-day solar rotations. This coronal hole has sustained for several rotations and continues to grow in size.
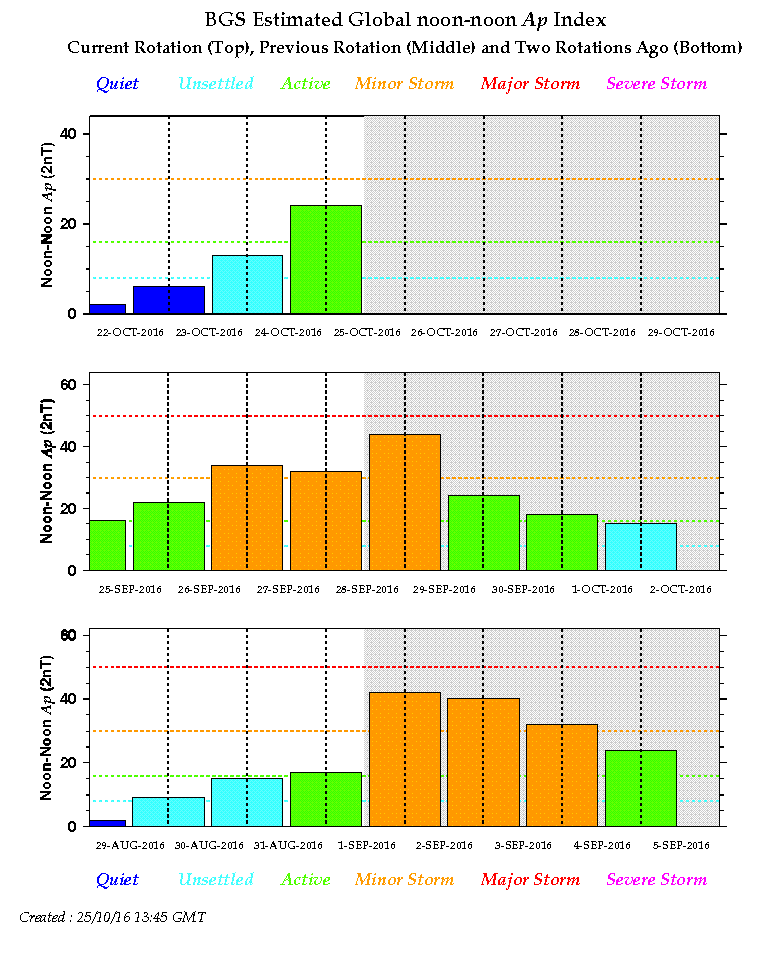
The previous two occurances of this coronal hole resulted in enhanced geomagnetic activity. Prolonged periods of STORM G1 (Kp=5) with periods of STORM G2 (Kp=6) were recorded at our UK magnetometers and at magnetic observatories around the world. There were several aurora sightings - although in the UK the clouds hampered viewing in many areas.
This high-speed solar wind stream is expected to elevate geomagnetic activity levels for several days. Activity may peak over the night of the 25th - 26th but STORM periods are expected for the next 2-3 days.
Assuming clear dark skies, there is an increased chance of seeing the aurora, particularly for those in Scotland, northern England and Northern Ireland.
Sign-up to receive Geomagnetic Disturbance Alert emails.
Follow us on Twitter:
Follow @BGSauroraAlert for more occasional aurora alerts.
Follow @BGSspaceWeather for daily space weather forecasts.
Glossary
- BGS
- The British Geological Survey is one of the Natural Environment Research Council's Research Centres.
- Coronal Hole
- A region in the Sun’s outer atmosphere (corona) where hot material can flow unrestrained by its magnetic fields out into space.
- High Speed Stream
- A fast moving stream of solar wind, responsible for magnetic storms.
- Magnetogram
- The variation, minute by minute, of the strength and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field. Measured in units of nano-Tesla (for the strength of the field) or in degrees (direction of the field).
Solar Wind- The ever-present expansion of the Sun’s hot outer atmosphere into the solar system, which carries space weather within it.