Space Weather Alert - 6 June 2016
What Has Happened?
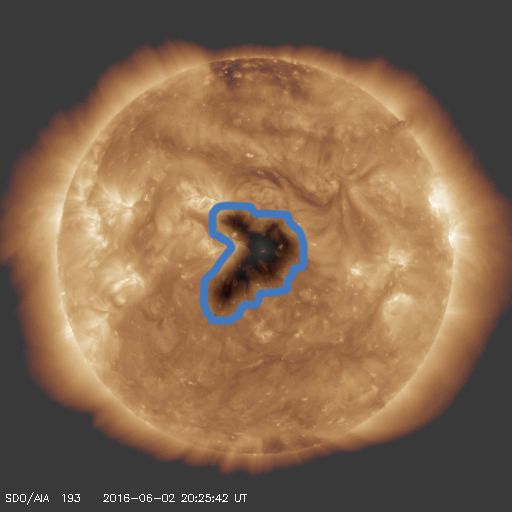
A large centrally located coronal hole on the solar disc is currently in an Earth-facing position. Its high speed solar wind stream is anticipated to arrive over the weekend. On the previous solar rotation (~28 days ago) this produced a moderate geomagnetic storm with a peak of STORM G2 and prolonged periods of STORM G1 (see NOAA space weather scales for more details about these storm levels).
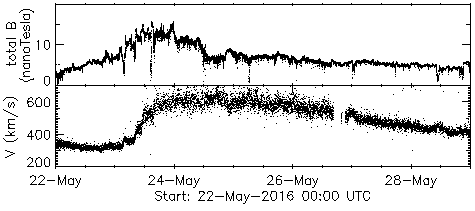
Observations from the STEREO-A spacecraft currently orbiting around the far side of the Sun sampled the coronal hole's solar wind stream half a solar rotation ago (~2 weeks ago). This indicated that similar levels of geomagnetic disturbance are likely this time around.
The high speed solar wind stream is expected to cause geomagnetic disturbances for around 24-48 hours before subsiding.
Assuming clear dark skies, there is an increased chance of seeing the aurora overnight during the weekend. Even though light northern evenings make it more difficult to see the aurora; those in Scotland, northern England and Northern Ireland would be likely to have the best chance given the expected geomagnetic activity levels.
Sign-up to receive Geomagnetic Disturbance Alert emails.
Follow us on Twitter:
Follow @BGSauroraAlert for more occasional aurora alerts.
Follow @BGSspaceWeather for daily space weather forecasts.
Glossary
- BGS
- The British Geological Survey is one of the Natural Environment Research Council's Research Centres.
- Coronal Hole
- A region in the Sun’s outer atmosphere (corona) where hot material can flow unrestrained by its magnetic fields out into space.
- High Speed Stream
- A fast moving stream of solar wind, responsible for magnetic storms.
- Magnetogram
- The variation, minute by minute, of the strength and direction of the Earth’s magnetic field. Measured in units of nano-Tesla (for the strength of the field) or in degrees (direction of the field).
Solar Wind- The ever-present expansion of the Sun’s hot outer atmosphere into the solar system, which carries space weather within it.